Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Clash of the Titans in Project Management
- What is PMP?
- What is Six Sigma?
- PMP vs Six Sigma: A Side-by-Side Comparison
- Lean Six Sigma vs PMP: The Lean Factor
- Which Certification Pays More?
- Job Roles Requiring PMP or Six Sigma
- Hybrid Approach: Combining PMP and Six Sigma for Maximum Impact
- Industry-Specific Demand: Where PMP and Six Sigma Matter the Most
- Exam Preparation Strategies: PMP vs. Six Sigma Study Techniques
- Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Choosing PMP or Six Sigma
- How AI and Automation Are Changing PMP and Six Sigma Practices
- 10 Less Commonly Known Facts About PMP & Six Sigma
- Final Thoughts: Which Certification Should You Choose?
- FAQs
Introduction: The Clash of the Titans in Project Management
If PMP and Six Sigma were superheroes, one would be the wise strategist ensuring projects meet deadlines, while the other would be the perfectionist eliminating every flaw. But in the battle of PMP vs Six Sigma, which one emerges victorious? If you're staring at these two giants wondering which certification will skyrocket your career, you're in the right place. Let's break it down, no boring jargon—just pure insights.

What is PMP?
PMP (Project Management Professional) is a globally recognized certification offered by the Project Management Institute (PMI). It validates expertise in project management methodologies, frameworks, and best practices.
Key Features of PMP Certification
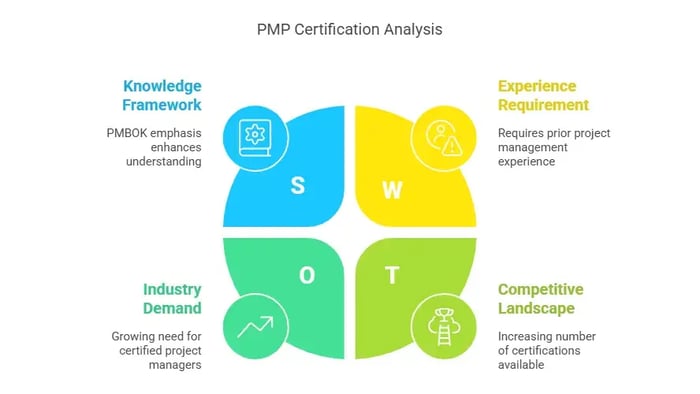
Emphasizes the PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge)
Focuses on time, cost, scope, and resource management
Industry-agnostic: Useful across IT, construction, healthcare, etc.
Requires project management experience
If you're considering Project Management Certification, PMP is a globally recognized credential that validates your expertise in managing projects efficiently.
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology focused on reducing defects and improving processes. Originally developed by Motorola, it has since become a standard for operational excellence.
Key Features of Six Sigma Certification
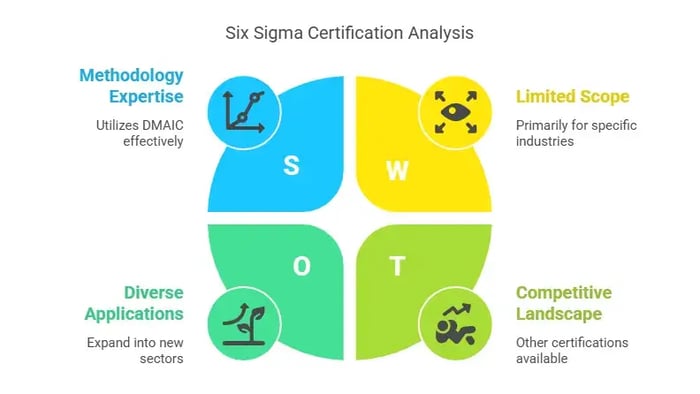
Uses the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology
Focuses on statistical process control to reduce variation
Best suited for manufacturing, healthcare, and finance
Comes in different belt levels: White, Yellow, Green, Black, and Master Black Belt
To enhance your process improvement skills, obtaining a Six Sigma Certification can help you drive quality and operational excellence in any industry.
PMP vs Six Sigma: A Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | PMP | Six Sigma |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Project execution & leadership | Process improvement & defect reduction |
| Best For | Managers handling multiple projects | Process experts improving efficiency |
| Certification Authority | PMI | ASQ, IASSC, etc. |
| Methodology | Predictive, Agile, Hybrid | DMAIC, Lean |
| Exam Difficulty | High (180 questions) | Varies by belt level |
Case Study: PMP in IT Project Management
A major tech company faced delays in software development due to poor resource allocation. A PMP-certified project manager introduced Agile methodologies, optimizing workflows, and reducing delivery times by 30%. The structured approach improved team collaboration and minimized project overruns.
Case Study: Six Sigma in Manufacturing
A leading automotive manufacturer used Six Sigma principles to reduce production defects. By implementing DMAIC, the company decreased error rates by 40%, saving millions in recall costs. The initiative also improved customer satisfaction and streamlined production efficiency.
These real-world applications highlight how PMP and Six Sigma cater to different but equally important aspects of business success.
| Feature | PMP | Six Sigma |
| Focus | Project execution & leadership | Process improvement & defect reduction |
| Best For | Managers handling multiple projects | Process experts improving efficiency |
| Certification Authority | PMI | ASQ, IASSC, etc. |
| Methodology | Predictive, Agile, Hybrid | DMAIC, Lean |
| Exam Difficulty | High (180 questions) | Varies by belt level |
Lean Six Sigma vs PMP: The Lean Factor
Lean Six Sigma integrates Lean methodologies, making it a strong choice for businesses focused on continuous improvement. Unlike traditional Six Sigma, Lean Six Sigma prioritizes speed and waste reduction alongside quality control.
How Lean Six Sigma Differs from PMP?
PMP is about managing projects to meet deadlines and budgets.
Lean Six Sigma is about optimizing workflows to remove inefficiencies.
PMP is best for project managers, while Lean Six Sigma suits process analysts and quality experts.
Which Certification Pays More?
According to Glassdoor, PMP-certified professionals earn an average of $120,000 per year, whereas Six Sigma Black Belts earn around $110,000 per year. However, Six Sigma Master Black Belts can surpass PMP salaries depending on the industry.
Salary by Industry
| Industry | PMP Salary | Six Sigma Salary |
| IT | $130,000 | $115,000 |
| Manufacturing | $110,000 | $120,000 |
| Healthcare | $115,000 | $108,000 |
Job Roles Requiring PMP or Six Sigma
Understanding which industries and job roles demand these certifications can help you make a more informed decision.
Common Job Titles for PMP-Certified Professionals
Project Manager
IT Project Manager
Construction Project Manager
Program Manager
Engineering Manager
Common Job Titles for Six Sigma-Certified Professionals
Quality Manager
Process Improvement Specialist
Manufacturing Engineer
Operations Manager
Data Analyst
If your career path leans toward managing projects from start to finish, PMP is the better choice. If optimizing and improving processes is your goal, Six Sigma will serve you well.
Hybrid Approach: Combining PMP and Six Sigma for Maximum Impact
Many organizations are recognizing the benefits of integrating both PMP and Six Sigma methodologies to enhance project efficiency and process optimization. PMP-certified professionals ensure that projects are delivered on time and within scope, while Six Sigma experts focus on eliminating defects and improving quality.
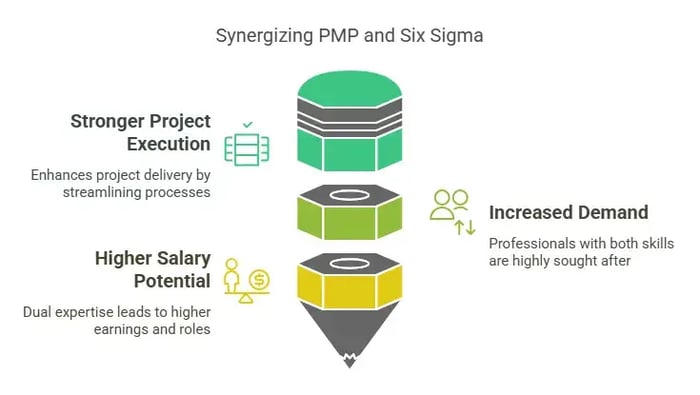
Why Combine Both?
Stronger Project Execution: Six Sigma helps streamline processes, reducing risks and inefficiencies in PMP-led projects.
Increased Demand: Many top employers prefer professionals who have expertise in both project management and process improvement.
Higher Salary Potential: Professionals who hold both certifications often command higher salaries and leadership positions.
For example, a PMP-certified project manager leading a large IT project can use Six Sigma principles to identify bottlenecks and improve team efficiency, ensuring timely project completion with optimal quality.
Industry-Specific Demand: Where PMP and Six Sigma Matter the Most
While both certifications are valuable, their demand varies by industry. Understanding where each excels can help professionals make informed career choices.

Industries Preferring PMP
Information Technology (IT): PMP helps manage software development, infrastructure upgrades, and Agile methodologies.
Construction & Engineering: Essential for managing large-scale infrastructure projects.
Finance & Banking: Ensures smooth execution of large financial initiatives and compliance projects.
Industries Preferring Six Sigma
Manufacturing: Focuses on defect reduction and process efficiency.
Healthcare: Improves patient care processes and reduces medical errors.
Logistics & Supply Chain: Enhances operational efficiency and reduces waste.
Professionals should consider the industry they wish to work in before deciding on a certification.
Exam Preparation Strategies: PMP vs. Six Sigma Study Techniques
Preparing for PMP and Six Sigma exams requires different approaches, given their unique methodologies.
PMP Study Techniques
PMBOK Guide Mastery: Focus on understanding PMI’s project management framework.
Mock Tests: Practice with scenario-based questions to improve decision-making.
Time Management: Since the exam consists of 180 questions in 230 minutes, time management is crucial.
Six Sigma Study Techniques
Statistical Analysis: Learn data-driven techniques like process mapping and regression analysis.
Hands-on Projects: Many Six Sigma certifications require real-world process improvement projects.
Belt-Level Specific Preparation: Study content varies significantly from Green Belt to Black Belt.
Choosing the right study approach can improve pass rates and exam confidence.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Choosing PMP or Six Sigma
Professionals often make mistakes when deciding between PMP and Six Sigma. Here are common pitfalls to avoid:
Mistake #1: Choosing Based on Popularity, Not Career Goals
Solution: Align certification choice with career objectives rather than trends.
Mistake #2: Underestimating Exam Difficulty
Solution: PMP and Six Sigma exams require significant preparation. Take mock exams and training courses.
Mistake #3: Ignoring Industry Demand
Solution: Research job postings to see which certification is more valuable in your industry.
Avoiding these mistakes ensures you select the certification that truly benefits your career.
How AI and Automation Are Changing PMP and Six Sigma Practices
The rise of AI and automation is transforming both project management and process improvement.
AI’s Impact on PMP
Predictive Analytics: AI helps project managers forecast risks and resource needs.
Automated Task Management: AI-driven tools optimize scheduling and project tracking.
Improved Communication: AI chatbots assist with stakeholder management.
AI’s Impact on Six Sigma
Real-Time Process Monitoring: AI analyzes live data to detect inefficiencies.
Advanced Statistical Analysis: AI automates complex data calculations, improving accuracy.
Automated Defect Detection: AI in manufacturing reduces quality control efforts.
Professionals must adapt to these technological advancements to stay competitive.
10 Less Commonly Known Facts About PMP & Six Sigma
PMP was first introduced in 1984.
Six Sigma was developed by Motorola in 1986.
Six Sigma belts are inspired by martial arts rankings.
PMP exam has changed formats multiple times.
Six Sigma was adopted by GE in the 1990s.
Lean Six Sigma evolved from Toyota’s manufacturing principles.
PMP-certified professionals earn 20% more on average – Salary data
Six Sigma uses a statistical method called ‘Standard Deviation’ – Statistical analysis
PMP requires a 35-hour project management course before the exam.
Six Sigma is widely used in healthcare to reduce medical errors – Healthcare case study
Final Thoughts: Which Certification Should You Choose?
If you’re looking to lead projects across various industries, go for PMP. If your passion lies in process optimization and eliminating inefficiencies, Six Sigma is the way to go. But why choose just one? Many professionals opt for both certifications to maximize career opportunities.
Looking to get certified in project management? Check out APMIC for the best Project Management Certifications tailored to your career goals.
FAQs
Is PMP harder than Six Sigma?
Yes, PMP is generally considered harder due to its broad scope and complex exam structure.
Can I do both PMP and Six Sigma?
Absolutely! Many professionals combine PMP’s project leadership skills with Six Sigma’s process improvement expertise.
Which certification is more recognized globally?
PMP is more recognized globally across industries, while Six Sigma is primarily valued in manufacturing and healthcare.
Do Six Sigma and PMP require renewal?
Yes, PMP requires renewal every three years, while Six Sigma renewals depend on the certification body.
Is PMP or Six Sigma better for IT professionals?
PMP is better for IT project managers, while Six Sigma benefits IT process improvement specialists.
Does Six Sigma help in Agile project management?
Yes, Lean Six Sigma integrates well with Agile methodologies for continuous process improvement.
How long does it take to get PMP vs Six Sigma?
PMP takes around 2-3 months of preparation, while Six Sigma certifications vary from a few weeks to several months depending on the belt level.
What industries prefer PMP over Six Sigma?
PMP is preferred in IT, construction, finance, and healthcare, while Six Sigma dominates manufacturing and logistics.





